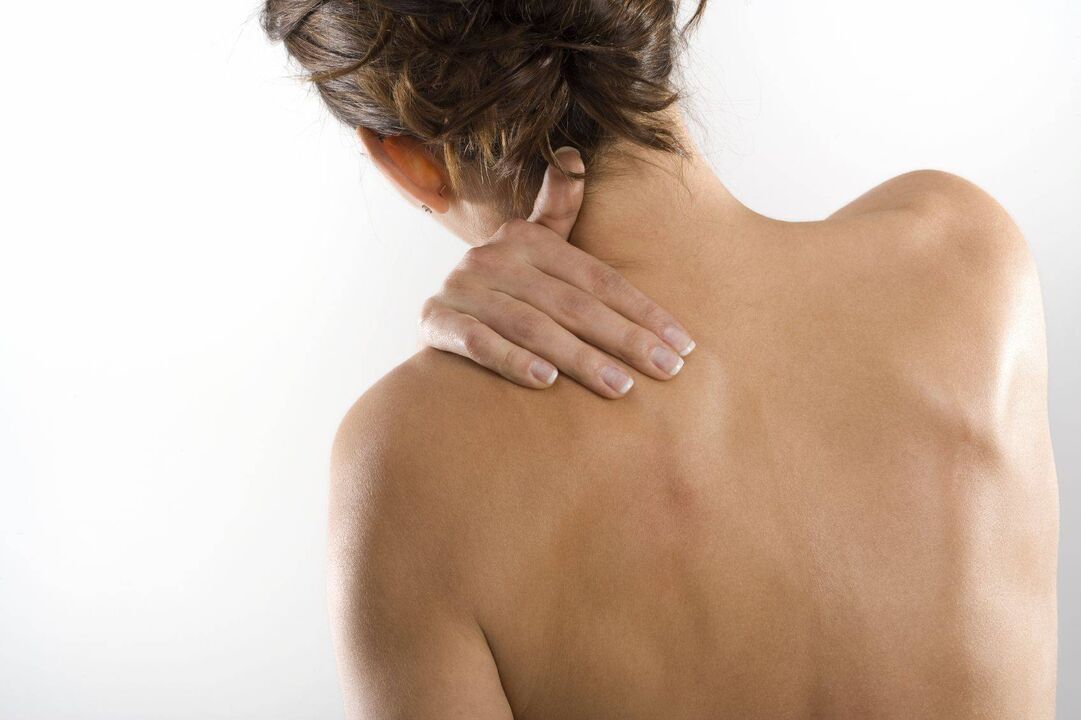
Osteochondrosis is a spine problem that affects every fourth inhabitant of the planet, at least according to the experts of the WHO Statistics Center.
In the first five most common diseases in the world, osteochondrosis takes the "honorable" third place, only cardiovascular diseases are ahead of it. In 2012, the media giant of the British Broadcasting Corporation, the BBC, published medical research data that was simply shocking: more than 5 million people die every year due to physical inactivity, that is, diseases caused by a sedentary lifestyle. A veritable pandemic of reduced physical activity has now covered one-third of the globe, and the latest scientific results prove that the culprit of many health-threatening diseases is not genetic predisposition or viruses, but an unhealthy lifestyle. Almost all back problems - intervertebral tears (hernias), osteoporosis, osteochondrosis and many other diseases related to osteochondrosis - are the result of sitting for many hours, whether in front of the TV, behind the desk or in the car seat. About 80% of all causes of the development of back and spine diseases are related to elementary degenerative changes in the muscle corset and the lack of full-fledged reasonable physical activity.
Osteochondrosis and spine
The structure of the spine is basically the same in both animals and humans. However, the proud title of Homo erectus, that is, Homo erectus, belongs only to man. Until recently, it was believed that upright posture was the main cause of pathological changes in the spine. As if the vertical position of the body causes an incorrect, uneven load on the spine. The static load to which the spine and sacrum, which consists of five vertebrae, is most exposed, is the most dangerous in terms of destructive effects on the intervertebral tissues. dynamic load, which is characterized by movements, affects the cervical spine. The structure of the spine is quite complex, it consists of many vertebrae - discs, connected by cartilage tissue. Discs, in turn, are multi-layered rings with a fluid core in the middle, which act to absorb shock when the spine is moved. In addition, the vertebrae are connected to a large number of muscles and other tissues. The flexibility of this entire connective system ensures the normal position of the spine. Simply put, the more flexible and adaptive the intervertebral discs are, the more flexible and healthy the spine is, the less the risk of osteochondrosis hitting it. Today, the theory that upright posture is responsible for all degenerative diseases of the spine is disputed. Merciless statistics convince clinicians that more inactivity, physical inactivity is a factor that provokes spinal diseases associated with dystrophy and degeneration of intervertebral tissues. In addition, excess weight, which actually increases the load on the discs, can aggravate the destructive processes and provoke osteochondrosis. Conclusion: movement is life. The statement is not new, it seems painfully wrong, trite, but does not require proof. A vivid example of how physical activity and flexibility can be the basis for the health of the spine are examples of people who regularly engage in gymnastics, yoga and other forms of physical education. Nature itself allows children to be flexible, because children's spinal discs are very flexible, only the disc nuclei contain up to 80% of liquid. With age, the amount of life-giving "lubrication" can decrease, but it can be preserved by consciously doing simple exercises and following the elementary rules of a healthy lifestyle. Osteochondrosis is a disease of people who have to sit or lie for hours or years, regardless of duty or free will, due to obligation, laziness or simply ignorance.
What is osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis is a concept that includes all degenerative and dystrophic changes in the spine. It should be noted that there is not a single word about osteochondrosis in the European version of the classification of diseases, where such diseases are classified as rheumatic and dorsopathic. In ICD-10, since 1999, a group of diseases with typical manifestations in the form of pain in the spine, which are not really related to visceral causes, is defined as dorsopathy. Osteochondrosis, registered as dorsopathy, in turn, is divided into three large groups:
- Deforming diseases, dorsopathy - scoliosis, lordosis, kyphosis, subluxation, spondylolisthesis.
- Spondylopathy - spondylosis, ankylosing spondylitis, and other ossifying dystrophic pathologies that limit the mobility of the spine.
- Other, other dorsopathies are degenerative changes accompanied by tears, protrusions.
Thus, osteochondrosis or osteochondrosis (from the Greek words - bone, cartilage and pain) is a general name for all problems caused by degeneration and malnutrition (degeneration and dystrophy) of paravertebral tissues in the spine. When deformed, the intervertebral shock-absorbing disc becomes thinner, flattened, which causes the spine to overload and become more deformed to the extent that the spine begins to deviate from its normal limits. With such a pathology, the nerve roots are compressed, inflamed, and pain appears.
Osteochondrosis affects almost the entire back, and the disease is called in clinical practice, depending on which part of the spine suffers more.
The most "famous" known to many is lumbar osteochondrosis, there is also a cervical definition that takes the second place in terms of prevalence, there are sacral, thoracic and widespread osteochondrosis. There are also cross pathologies - lumbosacral or, for example, cervicothoracic.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis can be very diverse, but sooner or later they all increase and manifest clinically. Of course, it is easier and faster to treat osteochondrosis in the early stages of its development, when the following symptoms are noticeable:
- Painful, dull aching sensations in the part of the spine affected by the degenerative process.
- Chronic muscle tension (especially characteristic of cervical osteochondrosis).
- Cracking when turning the body, neck.
- Headache, including tension headache (with cervical osteochondrosis).
- Painful pain in the chest, often reminiscent of cardiac pain (with thoracic osteochondrosis).
Osteochondrosis in the inflammatory stage has symptoms that force a person to consult a doctor, because they cause more obvious concern:
- Radiating pain in the limbs.
- Numbness of fingers or toes.
- Radiating pain to the fingertips of the extremities.
- Severe pain in the spine while performing simple physical activities.
- Pain that increases with small pushes, for example, shaking when traveling in transport.
- Inability to perform simple tasks involving rotation or bending of the body.
- General limitation of mobility, motor activity.
There are many factors that can cause problems with the spine, called osteochondrosis, but the already mentioned hypodynamia is in the first place. Other causes include:
- Functional - monotonous work, maintaining the same posture.
- Biomechanical - flat feet, congenital anomalies in the development of the spine.
- Hormonal - changes in hormonal levels due to age-related changes.
- Infectious - dystrophy of the intervertebral medium caused by the inflammatory process.
- Metabolic - overweight or underweight.
Factors that provoke osteochondrosis, that is, deformation and dystrophy of intervertebral discs, as a rule, act in combination and are almost never isolated.
The development of osteochondrosis is divided into the following stages:
- Changes in disc biomechanics as a result of tissue degeneration and dystrophic changes. This is the preclinical stage, if any, the symptoms are very weak, they do not show themselves. At this stage, the fibrous ring surrounding the disc begins to stretch or, conversely, shrink.
- The second stage is characterized by more instability of the disc, the fibrous ring does not stretch, its fibers become stratified, the ring begins to break. Due to the disruption of the nerve roots, pain appears in the spine, degenerative changes progress. Collagen tissue continues to break down, the normal height of the intervertebral space decreases.
- The disc is often completely ruptured, this pathology is accompanied by inflammation, herniation and disruption of nerve endings. Prolapse not only causes characteristic pain in the damaged area of the spine, but also affects the limbs and nearby parts of the body.
- The most difficult stage when spondylosis and other compensatory diseases of the spine join dystrophy. Often, the vertebra is adjusted to compensate for the lost functions, and the elastic tissue of the fibrous ring is gradually replaced by scar tissue and bone growth.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
From schoolchildren to the elderly, almost everyone associated with intellectual activity suffers from one or another form of cervical spine osteochondrosis. Osteochondrosis of the cervical region is considered a disease associated with an increase in dynamic loads, which leads to the degeneration of intervertebral discs and their collapse. The hardening and growth of the cartilage tissue leads to a violation of the damping properties of this part of the spine, head movements - bends, circular movements, turns become difficult and are accompanied by characteristic signs of osteochondrosis.
In the early stages of the development of the disease, the symptoms that can cause osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are not specific and resemble the symptoms of other pathologies not related to the skeletal system. The list of manifestations of osteochondrosis, which must be differentiated and specified in order to determine the correct diagnosis, is as follows:
- Severe headaches similar to migraine attacks.
- Headache extending from occiput to neck.
- Headache aggravated by coughing, turning the head, sneezing.
- Headache that radiates to the chest or shoulder.
- Dizziness, sensory disturbances - double vision, difficulty concentrating. Noise in the ears, in advanced cases, impaired coordination of movements.
- Symptoms similar to cardiac pain, especially with pain in angina pectoris - heart pain under the shoulder blade, extending to the cervical region or arm. Pain may increase and is not relieved by taking heart medications.
- Hypertension-like pain (heaviness in the back of the head).
Consequences and complications
Before treating osteochondrosis, like any other disease, it is necessary to find its causes, which is very difficult when it comes to degenerative pathologies of the spine. The factors that cause deformation of the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine are associated with the anatomical features of this zone. The cervical vertebrae are almost constantly under tension due to insufficient general motor activity. Given the general "sedentary" lifestyle of more than half of the working population, the problem sometimes becomes insurmountable. In addition, the cervical vertebrae are smaller than the vertebrae of other regions of the spine, and the internal canal is narrower. A large number of nerve endings, a large number of blood vessels, the presence of the most important artery that feeds the brain - all this makes the cervical region extremely sensitive. Even the smallest narrowing of the intervertebral space leads to disruption of the nerve roots, swelling, inflammation and, accordingly, deterioration of blood supply to the brain. Often, a decrease in mental activity is due to the fact that a person develops osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. There's a not-so-distant historical anecdote in which Margaret Hilda Thatcher chastised her staffer with these words: "Your problem isn't your headache or your view of the issue on the ballot. It's that your spine isn't connected to your brain, John. "this famous quote perfectly characterizes the condition that sometimes causes osteochondrosis of the cervical spine - the spine does not provide the proper "feeding" of the head. When it comes to "feeding", in fact, not only the canal of the spinal cord, but also the canal of the artery passing through the transverse nerve processesis involved. The vertebral artery goes to the skull to feed the cerebellum, and this artery also supplies the vestibular apparatus with nutrients and oxygen. The slightest disturbance of blood flow through these channels can either provoke or aggravate the course of the vegetative-vascular syndrome. In addition to VSD, cervicalosteochondrosis of the region causes typical symptoms of radicular syndrome (sciatica), pain in the tips of the fingerspallor of the skin (marbling) is evident when it spreads to the bee or a finger. One of the most unpleasant complications caused by cervical osteochondrosis is palmar fibromatosis, also called Dupuytren's contracture. With this disease, the palmar aponeurosis (tendon plate) is affected and the bending function of the fingers is disturbed.
Diagnosis of cervical spine osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is diagnosed by a specialist based on the patient's complaints and can be confirmed and clarified using X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging, computer tomography.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Complete treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is possible only in its initial stages, but it is possible to save a person from the painful symptoms of this disease, prevent exacerbations and get rid of some pathological changes in the spine. Therefore, we must not forget the importance of timely treatment of the disease.
How to treat osteochondrosis?
Treating osteochondrosis is not easy, as a rule, therapy is prescribed as comprehensively as possible, including all the means available in modern medicine. In addition to conservative drug treatment, proven phytotherapeutic preparations, acupuncture, a set of therapeutic exercises, and sometimes surgical operations to remove hernias and subluxations of the vertebrae are used. It should be recognized that osteochondrosis and treatment are two concepts that a sick person will encounter for quite a long time, sometimes throughout his life. In addition to the initial stage aimed at eliminating the pain symptom, the therapy includes permanent restorative, rehabilitation and preventive measures. Complex, multicomponent diseases are always treated for a long time. If a diagnosis is made - osteochondrosis, how to treat it - this is the first question that is solved not only by the doctor, but also by the patient himself, because his direct participation and responsible compliance, the fulfillment of all prescriptions often play a decisive role. role in recovery.
What to treat?
The list of the most commonly used drugs for the treatment of osteochondrosis:
- A complex, effective homeopathic preparation that should be used for a long time, like any other homeopathy (in ampoules or in the form of tablets).
- An effective external remedy that relieves muscle and joint pain.
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal agent (in the form of an ointment - externally, in tablets - orally).
- Ointment of complex effects from the category of homeopathic remedies.
- A drug in the form of tablets from the category of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
- A drug from the category of glucocorticoids.
- Ointment from the category of external anti-inflammatory non-steroidal agents.
- Gel from the category of external non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- A drug from the category of external anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs.
If we summarize everything that involves the treatment of a disease such as osteochondrosis, the treatment can be divided into the following stages and types:
- The use of NSAIDs - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - is considered the gold standard in the treatment of all degenerative and dystrophic pathologies of bone and muscle systems. The first thing these drugs do is reduce the symptom of pain, and the second is to significantly reduce inflammation.
- Medicines called myelorelaxants can actually effectively relieve muscle cramps and spasms.
- Traction therapy is traction therapy. In this rather painful but effective process, there is a gradual stretching of the tissues and muscles surrounding the vertebrae, accordingly, the intervertebral distance increases and approaches the norm.
- Biogenic drugs, vascular agents that nourish the dystrophic areas of tissues, B vitamins restore the functional abilities of the deformed spine well.
- Sedative drugs that normalize the state of the nervous system. Perfectly relieves muscle tension and nerve endings from acupuncture.
- Physiotherapy procedures - electrophoresis, phonophoresis, UHF, massages, mud procedures, balneotherapy, magnetotherapy.
- During the recovery period, the correction of the spine is carried out using manual therapy.
- Treatment of osteochondrosis includes constant exercises from a complex of physiotherapy exercises.
In the most extreme cases, when the course of osteochondrosis enters the final stage, surgical intervention in the area of localization of the inflammatory process is indicated. Often the hernia is operated, and it is also possible to remove the deformed bone tissue of the neighboring vertebrae.
Where can osteochondrosis be treated?
Self-treatment of almost all diseases is a trend observed in almost all countries, but it is characteristic of post-Soviet countries, where the traditional health care structure is still changing. Confused with innovation, often simply out of ignorance, many of us try to deal with back, neck or lower back pain on our own. Although this time is not very effective, you can call it the first stage of treatment, because osteochondrosis needs to be treated only with the help of a doctor. The second stage, when independent actions do not lead to the desired, permanent result, a person thinks about visiting a doctor and the question arises, osteochondrosis - how to treat, how to treat and most importantly, where to treat osteochondrosis.?First, you can contact a local therapist, who will most likely send the patient for examination - X-rays, blood tests and refer to a neurologist. Secondly, you can immediately make an appointment with a neurologist, at least undergo an X-ray examination of the entire spine before the consultation. In no case should you go to extremes and look for an experienced massage therapist, any massage, first of all, involves an initial examination of the condition of the body, especially the condition of the spine. Vertebrologists and vertebroneurologists - doctors specializing in spine diseases - deal with the problem of osteochondrosis.
Osteochondrosis is a complex disease, but the examples of many people who have overcome even severe spinal injuries prove that everything is possible and achievable. The main thing is to analyze our motor activity in the first alarming signals that the back gives us and take appropriate measures. You can immediately go to the doctor and start treatment, or if the disease has not progressed, you can start to act, because as Aristotle, the teacher of Alexander the Great, who was extremely active, said, "Life requires action and is necessary. , otherwise it is not life".
What does history say about osteochondrosis?
The etiology of osteochondrosis is still not clear, moreover, despite the clear ancient origin of this disease, diseases of the spine began to be treated seriously only in the 18th century. Since then, debates and discussions about the real "enemy" that causes degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs have not stopped. Meanwhile, long ago, even in the time of Hippocrates, there were treatises on bone cutting, which suggests that the ancient Hellenes also suffered from back pain. Hippocrates himself was so interested in spinal issues that he conducted medical experiments that are dubious from a modern point of view: his students tied the patient's hands and feet neatly behind his back in a horizontal plane, and stretched his limbs too far. as possible. Then the great healer stood on the sufferer's back and began to walk over him. The founder of medicine was sincerely convinced that such fixation, traction and massage, according to the ancient Greek sages, would restore the health of the spine, which is the key to many happy people. The systematization of some methods explaining how to treat osteochondrosis began only at the end of the 17th century. At the same time, terminology appeared that formalized the applied fields in medicine, including bone structure. Two centuries later, it was divided into chiropractic and osteopathy. The first direction was purely practical, using power techniques, osteopaths were more theoreticians and researchers. Manual therapy gradually appeared at the intersection of these sciences, without which the treatment of osteochondrosis is almost unthinkable today.
As for the term defining the disease "osteochondrosis", a typical story happened for osteochondrosis, which is characteristic of other diseases of uncertain etiology. As soon as it was said - and lumboischialgia, and sciatica and Schmorl's hernia, and sciatica and spondylosis. It took almost a century for doctors to understand osteochondrosis and come to a consensus.

















































